To enable single sign-on in Office 365 and a variety of other applications you need to provide a federated authentication system. Microsoft’s free server software for this is currently Active Directory Federation Server 2.0 (ADFS), which is downloaded from Microsoft’s website.
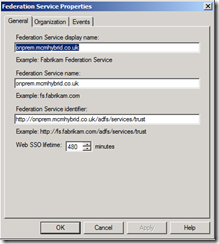
ADFS is installed on a server within your organisation, and a trust (utilising trusted digital certificates) is set up with your partners. If you want to authenticate to the partner system from within your environment it is usual that your application connects to your AFDS server (as part of a bigger process that is better described here: http://blogs.msdn.com/b/plankytronixx/archive/2010/11/05/primer-federated-identity-in-a-nutshell.aspx). But if you are outside of your organisation, or the connection to ADFS is made by the partner rather than the application (and in Office 365 both of these take place) then you either need to install ADFS Proxy or publish the ADFS server through a firewall.
This subject of the blog is how to do this via ISA Server or TMG Server. In addition to configuring a standard HTTPS publishing rule you need to disable Link Translation and high-bit filtering on the HTTP filter to get it to work.
Here are the full steps to set up AFDS inside your organisation and have it published via ISA Server – TMG Server is to all intents and purposes the same, the UI just looks slightly different:
- New Web Site Publishing Rule. Provide a name.
- Select the Action (allow).
- Choose either a single website or load balancer or use ISA’s load balancing feature depending on the number of ADFS servers in your farm.
- Use SSL to connect:
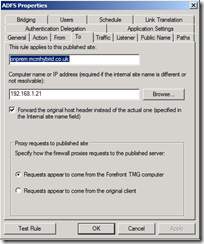
- Enter the Internal site name (which must be on the SSL certificate on the ADFS server and must be the same as the externally published name as well). Also enter the IP address of the server or configure the HOSTS files on the firewall to resolve this name as you do not want to loop back to the externally resolved name:
- Enter /adfs/* as the path.
- Enter the ADFS published endpoint as the Public name (which will be subject or SAN on the certificate and will be the same certificate on the ADFS server and the ISA Server):
- Select or create a suitable web listener. The properties of this will include listening on the external IP address that your ADFS namespace resolves to, over SSL only, using the certificate on your ADFS server (exported with private key and installed on ISA Server), no authentication.
- Allow the client to authenticate directly with the endpoint server:
- All Users and then click Finish.
- Before you save your changes though, you need to make the following two changes
- Right-click the rule and select Configure HTTP:
- Uncheck Block high bit characters and click OK.
- Double-click the rule to bring up its properties and change to the Link Translation tab. Uncheck Apply link translation to this rule:
- Click OK and save your changes.
ADFS should now work through ISA or TMG assuming you have configured ADFS and your partner organisations correctly!