Once you have installed Windows 7 RC and downloaded Microsoft Virtual PC you might have the need to run Microsoft Official Curriculum courseware virtual machines. And therein is a problem.
The virtual machines are built to use Virtual Server 2005, but that cannot install in Windows 7, so you cannot use the Lab Launcher. Though you can install the courseware drives, you will need to run the installer in compatibility mode or the VHD installer will not run.
Once you have the VHD files unzipped you need to configure Microsoft Virtual PC to load them up. This though is a problem if you are not located in the same timezone as the creators of the base disks (PST timezone).
The steps to create a virtual machine when you are in a different timezone are:
- Start the virtual machine wizard and make a note of the location value. You will need to modify files in this location later on
- Set memory and untick the network connections option
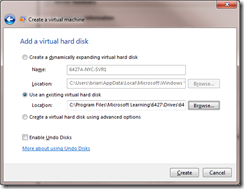
- Browse to the exiting hard disks folder. Enable undo disks at this time as well
- If you are in a different timezone you will get the following cryptic error
- Click OK and modify the file used to point to either any of the “allfiles” disks (as these are not differencing disks) or create your own empty vhd for the time being
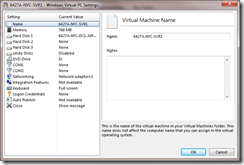
- Complete the creation steps and then bring up the settings of the new virtual machine (with the wrong disk attached)
- Modify the network settings to Internal Network and add any additional disks needed (this will be described in the full setup guide for the course) and close the settings dialog.
- Browse to the folder that contains the actual settings file (the vmc file). This folder is the location value from step 1 (defaults to C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows Virtual PC\Virtual Machines).
- Open the vmc file in Notepad (or an XML editor) and change the settings to that which you require. These changes are for disks. Look for ide_controller 0 and ide_controller 1 (if present) and change the name of the vhd file to the correct disk name.
- Modify the time sync. settings as per disabling-time-synchronization-under-virtual-pc-2007. The virtual machines from Microsoft for training purposes have a grace period and if you bring them up with the current date/time on them (which Virtual PC 2007 does automatically) then you will need to activate them.
- Save the file when your changes are completed.
- Start the virtual machine. You will see this error message - Inconsistency in virtual hard disk time stamp detected - The virtual hard disk's parent appears to have been modified without using the differencing virtual hard disk. Modifying the parent virtual hard disk may result in data corruption. It is strongly recommended that you mark the parent virtual hard disk as read-only to prevent this in the future. If you recently changed timezones on your host operating system, you can safely continue using this virtual hard disk.
- This can occur for a number of reasons, but if the reason is timestamps then click OK. DO NOT click the option not to show the message again, or you will not be able to get past this error without modifying the options.xml file in C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows Virtual PC.
The virtual PC will start, and will prompt you about updates to the integration components, but that is only a minor , so that can be ignored when you are presented with that error, unless you want the error to never show again per machine, in which case install (at your own risk and numerous reboots) the integration components.
Finally, you might need to reactivate some machines, as the hardware will have changed.